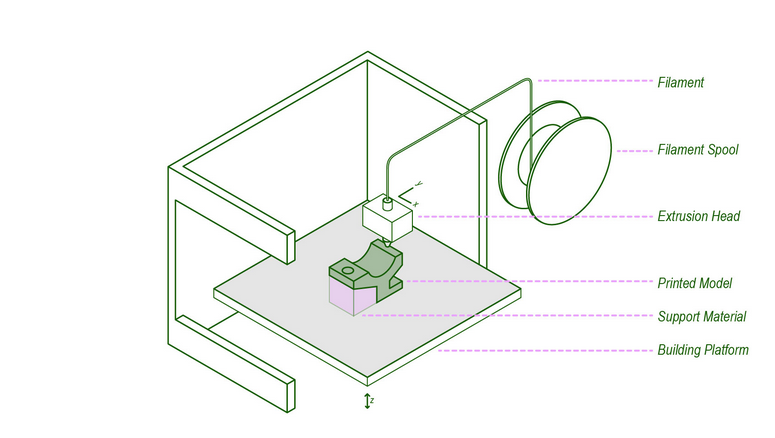
Material Extrusion (FDM/FFF):
Material Extrusion, also known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is one of the most common and accessible 3D printing technologies. It involves the extrusion of a thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle. The filament is melted and deposited layer by layer onto a build platform, following a predetermined path to create the object. As each layer cools and solidifies, subsequent layers are added until the complete object is formed.
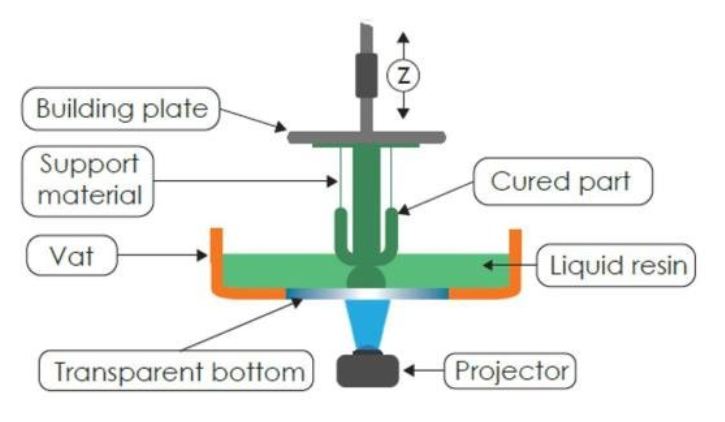
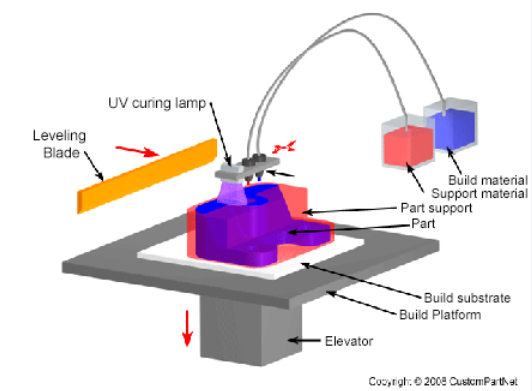
Vat Polymerization (SLA/DLP):
Vat Polymerization utilizes liquid photopolymer resin as the printing material. It involves a vat or tank containing the liquid resin, and a build platform immersed in the resin. Using selective curing, a light source, such as a laser or digital light projector, selectively exposes the resin to solidify it layer by layer according to the object’s cross-section. The build platform is gradually lifted or lowered to create the object as the layers are cured.
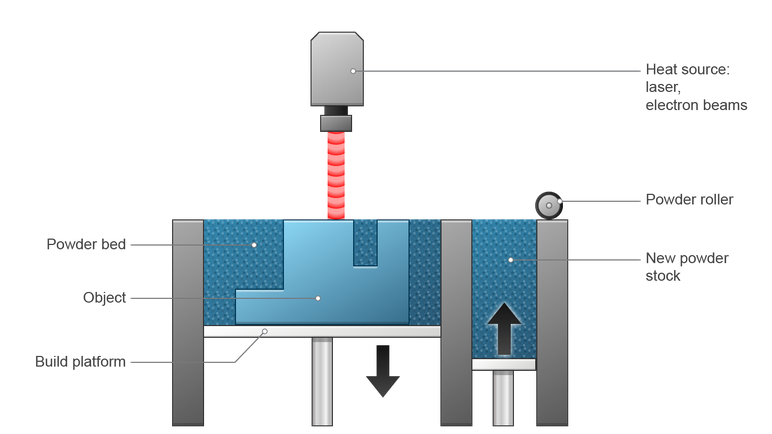
Powder Bed Fusion (SLS/DMLS/SLM):
Powder Bed Fusion encompasses several related technologies, including Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), and Selective Laser Melting (SLM). These methods involve spreading a thin layer of powdered material, such as polymers or metals, onto a build platform. A high-powered laser or electron beam selectively fuses or melts the powder according to the object’s shape and cross-section. The process is repeated layer by layer until the complete object is formed within the powder bed.
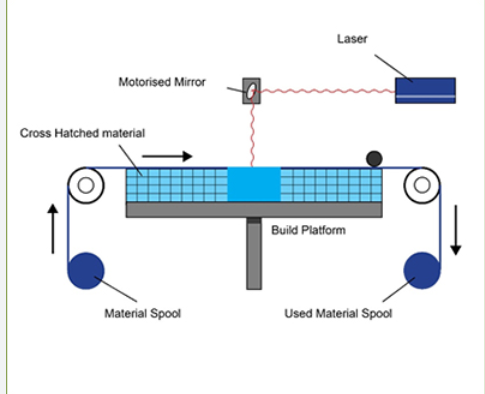
Material Jetting:
Material Jetting works similarly to traditional inkjet printing. Multiple print heads deposit small droplets of liquid photopolymer or wax material onto the build platform. The droplets are then cured or solidified using UV light or other curing methods to form each layer. The process is repeated, layer by layer, until the object is completed. Material Jetting allows for the use of different materials and can produce objects with high levels of detail and multiple colors.
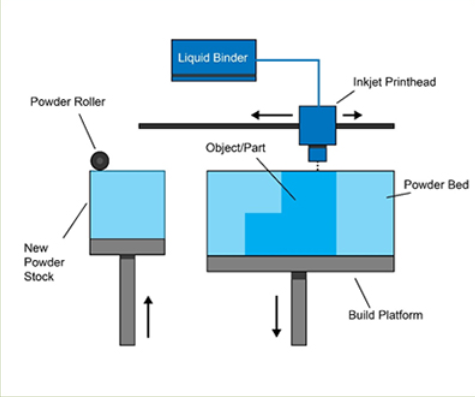
Binder Jetting:
Binder Jetting involves the selective deposition of a liquid binding agent onto a powdered material layer by layer. The liquid binder binds the particles together, forming each layer of the object. After printing, the object may undergo additional post-processing steps, such as curing or sintering, to strengthen and finalize its structure. Binder Jetting can work with a variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, and sand.
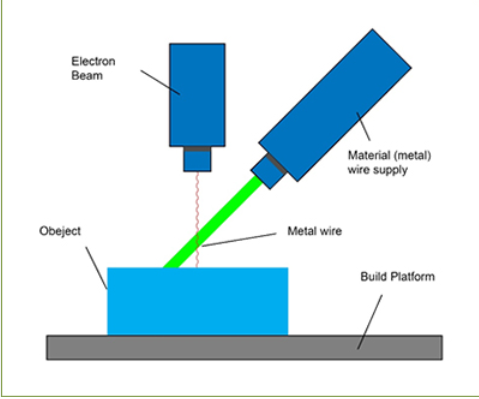
Directed Energy Deposition (DED):
Directed Energy Deposition is a 3D printing method that involves melting or sintering metallic or composite materials as they are deposited onto a substrate or previously printed layers. This process is achieved using a focused energy source, such as a laser or electron beam, which melts the material to form each layer. DED is often used for large-scale printing, repairs, or the addition of features to existing objects.
Sheet Lamination:
Sheet Lamination techniques involve bonding or laminating layers of sheet material together to create the object. This can include methods like laminated object manufacturing (LOM) or ultrasonic additive manufacturing (UAM). LOM uses layers of paper or other sheet materials that are cut and bonded together using heat or adhesive. UAM employs ultrasonic vibrations to bond layers of metallic foils together. Sheet Lamination can provide flexibility in materials and can be useful for creating large objects or prototypes.